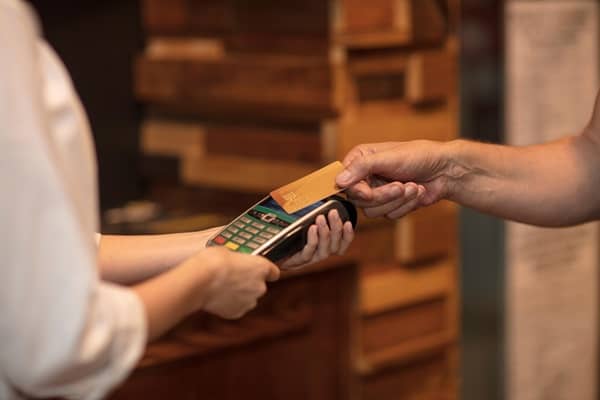
Moving to a new point-of-sale system can disrupt daily operations and confuse employees if not handled properly. Many businesses struggle with data transfer issues, staff confusion, and system downtime during the switch. These problems can lead to lost sales and frustrated customers.
On-site setup and training provide hands-on support that eliminates common migration problems by having experts guide staff through the new system in real-time. Professional technicians handle the technical setup while trainers work directly with employees to build confidence with the new features. This approach reduces downtime and gets businesses running smoothly faster than trying to figure things out alone.
The right support makes all the difference when switching to an all-in-one POS system. Smart planning and expert guidance help businesses avoid costly mistakes and get their teams up to speed quickly. The following best practices show how to make your POS migration successful from day one.
The role of on-site setup and training in POS migration
On-site setup and training serve as the foundation for successful POS system transitions by providing direct technical support and hands-on learning opportunities. These services help businesses maintain operations while employees learn new processes and systems.
Guaranteeing seamless system integration
On-site technical experts handle the complex process of connecting new POS hardware and software with existing business systems. They configure payment processors, inventory management tools, and accounting software to work together smoothly.
Technical specialists test all connections before going live. They verify that credit card readers, receipt printers, and barcode scanners communicate properly with the main system. This prevents payment failures and checkout delays on the first day of operation.
The setup team also transfers existing product data, customer information, and sales history from the old system. They check that all information appears correctly in the new system. This protects valuable business data and maintains customer service quality.
Network configuration requires special attention during installation. Technicians optimise internet connections and set up backup systems. They also establish security protocols to protect sensitive payment information.
Reducing downtime and operational disruption
Professional installers work during off-peak hours to minimise business interruption. They often complete major system changes overnight or during slow periods. This approach keeps sales flowing while the transition happens.
The installation team creates backup plans for potential problems. They bring spare equipment and have technical support ready. If issues arise, they can quickly switch to backup systems or contact remote support teams.
Training happens alongside installation to maximise efficiency. Staff members learn the new system while technicians fine-tune settings. This dual approach reduces the total time needed for complete system deployment.
Quick problem resolution keeps operations running smoothly. On-site experts can immediately fix hardware issues or software glitches. Remote support cannot match this speed for physical equipment problems.
Accelerating employee adoption
Hands-on training helps staff members learn faster than online tutorials or manuals. Trainers demonstrate each function while employees practice on actual equipment. This interactive approach builds confidence and reduces learning time.
Trainers adapt their teaching methods to different learning styles. Some staff members learn better through visual demonstrations, while others prefer step-by-step verbal instructions. Personal attention addresses individual questions and concerns.
Real-world scenarios prepare employees for actual customer interactions. Trainers simulate busy periods, difficult returns, and payment problems. This practice reduces stress and mistakes during actual operations.
Follow-up support continues after initial training ends. Trainers often return within the first week to answer questions and provide additional guidance. This ongoing support prevents small problems from becoming major issues.
Addressing custom business requirements
Every retail business has unique processes that require system customisation. On-site experts configure the POS system to match specific workflows and procedures. They set up custom product categories, pricing rules, and employee permissions.
Local regulations and tax requirements need proper configuration. Technicians program the correct tax rates and compliance features for each location. They also set up required reporting functions for government agencies.
Integration with specialised equipment requires hands-on setup. Some businesses use scales, time clocks, or security systems that connect to the POS. On-site technicians handle these complex connections and test all functions.
Staff training covers business-specific procedures and policies. Trainers learn about return policies, discount procedures, and inventory management before teaching employees. This targeted approach makes training more relevant and useful.
Best practices for effective on-site POS setup and training
Planning ahead, training each staff member based on their job duties, and testing all system components create the foundation for successful POS migration. These three areas work together to reduce downtime and help employees adapt quickly to new technology.
Pre-migration planning and assessment
Store managers should create a detailed timeline that begins 4-6 weeks before the migration date. This schedule must include staff training sessions, hardware installation, and system testing phases.
The assessment phase involves documenting current workflows and identifying potential challenges. Staff members should list their daily tasks and note which POS functions they use most often.
Key planning elements include:
- Staff availability for training sessions
- Peak business hours to avoid during setup
- Backup procedures for system failures
- Contact information for technical support
Store layouts require evaluation to determine optimal hardware placement. Cash registers, card readers, and receipt printers need adequate space and proper electrical connections.
Network infrastructure testing prevents connectivity issues during migration. Internet speed, Wi-Fi strength, and ethernet connections should be verified before installation begins.
Customising training for staff roles
Different job positions require different levels of POS system knowledge. Cashiers need basic transaction processing skills, while managers require access to reporting and administrative functions.
New employees should start with simple tasks like processing cash payments and printing receipts. Advanced features like inventory management and discount applications come after they master basic operations.
Training progression by role:
| Role | Basic Skills | Advanced Skills |
| Cashier | Process payments, print receipts | Handle returns, apply discounts |
| Supervisor | All cashier functions | Generate reports, manage users |
| Manager | All functions | System settings, troubleshooting |
Hands-on practice sessions work better than lecture-style training. Staff members should complete actual transactions using sample products and test credit cards.
Training sessions should last 30-45 minutes to maintain focus. Multiple short sessions spread over several days help employees retain information better than single long sessions.
Validating hardware and software configurations
All hardware components require individual testing before staff training begins. Cash drawers, barcode scanners, and receipt printers must connect properly to the main system.
Software settings need verification to match business requirements. Tax rates, payment processing options, and receipt formats should be configured according to store policies.
Test transactions using different payment methods help identify configuration problems. Cash, credit cards, debit cards, and mobile payments should all process correctly.
Hardware validation checklist:
- Cash drawer opens and closes properly
- Barcode scanner reads product codes accurately
- Receipt printer produces clear, readable receipts
- Card reader accepts chip and contactless payments
Network connectivity testing prevents system crashes during busy periods. Multiple devices should connect simultaneously without causing slowdowns or disconnections.
Backup procedures require testing to verify they work when needed. Data backup systems and alternative payment methods should be ready if the main system fails.
Conclusion
On-site setup and training create the foundation for successful POS migration. Proper installation by skilled technicians prevents technical issues that could disrupt daily operations.
Staff training during the setup process helps employees learn the new system quickly. This direct approach reduces confusion and builds confidence with the technology.
The combination of professional setup and hands-on training minimises downtime. Businesses can return to normal operations faster when both elements work together from the start.